| |
Nesting State Machines
Description: This tutorial gives an example of nesting a state machine in another state machine, creating a hierarchical state machine.Tutorial Level: BEGINNER
Next Tutorial: Concurrent States
All of the following examples can be run without modification. They can be found in the smach_tutorials package in the examples directory. The comments at the head of each file show roughly what the output from running the script should look like.
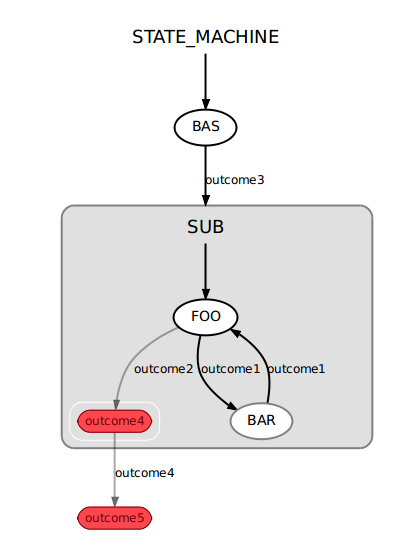
1 #!/usr/bin/env python
2
3 import roslib; roslib.load_manifest('smach_tutorials')
4 import rospy
5 import smach
6 import smach_ros
7
8 # define state Foo
9 class Foo(smach.State):
10 def __init__(self):
11 smach.State.__init__(self, outcomes=['outcome1','outcome2'])
12 self.counter = 0
13
14 def execute(self, userdata):
15 rospy.loginfo('Executing state FOO')
16 if self.counter < 3:
17 self.counter += 1
18 return 'outcome1'
19 else:
20 return 'outcome2'
21
22
23 # define state Bar
24 class Bar(smach.State):
25 def __init__(self):
26 smach.State.__init__(self, outcomes=['outcome1'])
27
28 def execute(self, userdata):
29 rospy.loginfo('Executing state BAR')
30 return 'outcome1'
31
32
33
34 # define state Bas
35 class Bas(smach.State):
36 def __init__(self):
37 smach.State.__init__(self, outcomes=['outcome3'])
38
39 def execute(self, userdata):
40 rospy.loginfo('Executing state BAS')
41 return 'outcome3'
42
43
44
45
46 def main():
47 rospy.init_node('smach_example_state_machine')
48
49 # Create the top level SMACH state machine
50 sm_top = smach.StateMachine(outcomes=['outcome5'])
51
52 # Open the container
53 with sm_top:
54
55 smach.StateMachine.add('BAS', Bas(),
56 transitions={'outcome3':'SUB'})
57
58 # Create the sub SMACH state machine
59 sm_sub = smach.StateMachine(outcomes=['outcome4'])
60
61 # Open the container
62 with sm_sub:
63
64 # Add states to the container
65 smach.StateMachine.add('FOO', Foo(),
66 transitions={'outcome1':'BAR',
67 'outcome2':'outcome4'})
68 smach.StateMachine.add('BAR', Bar(),
69 transitions={'outcome1':'FOO'})
70
71 smach.StateMachine.add('SUB', sm_sub,
72 transitions={'outcome4':'outcome5'})
73
74 # Execute SMACH plan
75 outcome = sm_top.execute()
76
77
78
79 if __name__ == '__main__':
80 main()







